
Updated : September 23, 2025
Are you bothered by high call abandonment? Are your customers complaining about long wait times? And are your agents tired of high attrition rates and burnout?
80% of customers say that the experience a company provides is as important as its services. A study indicates that after a long wait, 60% of customers will never call back. And 32% will not return if they abandon your call.
No organization wants to lose sales with poor customer experience. Effective call center management can help you improve your customer experience and deliver quality service. Here’s what you need to know.
What Is Call Center Management?
Call center management is the process of looking after the daily operations of a call center. It usually includes managing processes, staff, technology, and strategies to meet business goals and maintain performance.
There are certain key aspects of call center management:
- Process Improvement: Call center managers work closely with their teams. They identify what works well and where they can make improvements for both agents and customers.
- Training and Staffing: It means to find the right people for your call center team, bring them on board smoothly, and help them develop the skills they need to handle customer conversations with confidence.
- Compliance and Quality Assurance: Your team needs to deliver great service. It needs to stay within the guidelines and regulations to keep your company and customers protected.
- Performance Monitoring: Managers track important metrics to see how calls go, support agents to reach their goals, and make sure customers have positive experiences.
- Integration of Technology: Your operations team must keep systems running smoothly and bring in helpful tools like smart analytics, call routing features, and customer service platforms that make everyone’s job easier.
Key Responsibilities In Managing A Call Center
To manage call center operations, two main leadership roles are important. Each has different responsibilities, but they work together to create a successful operation.
1. For Manager
A call center manager focuses on the broader organizational perspective. Their role centers on strategy. They develop plans, oversee budgets, and make decisions. Here’s what consumes most of their time as a manager:
- Strategic Planning and Goal Setting: They establish the overall vision for your call center. They evaluate business requirements, define performance benchmarks, and develop policies that balance customer satisfaction with business outcomes.
- Budget Management and Resource Allocation: They oversee financial resources. They need to manage personnel costs, technology expenditures, and operational expenses. They must balance and deliver quality service and maintain fiscal responsibility. They need to make difficult choices regarding staffing levels or system upgrades.
- Hiring and High-Level Training Decisions: They are accountable for team development. They create recruitment approaches, authorize training initiatives, and make decisions about career advancement and separations. They establish expectations for the caliber of professionals representing your organization.
- Performance Analysis and Reporting: They monitor key indicators and communicate outcomes to senior leadership. They examine patterns, spot challenges, and recommend improvements. Their insights shape organizational decisions about customer service approaches.
- Compliance and Risk Management: They ensure that the complete operation adheres to industry standards and organizational protocols. This encompasses supervising security measures, upholding service excellence, and addressing any regulatory or compliance concerns.
2. For Supervisor
Supervisors serve as the connection between leadership and frontline staff in a contact center. They manage daily activities and interact directly with floor teams. The primary responsibilities as a supervisor in a call center environment include:
- Daily Operations Management: They ensure seamless daily functioning. This involves tracking live performance data, modifying staffing levels as required, and addressing any urgent situations that arise. When technical systems fail or call traffic increases unexpectedly, they coordinate the response.
- Direct Agent Coaching and Development: They collaborate individually with agents to enhance their capabilities. They facilitate regular mentoring sessions, offer call-specific guidance, and support agents’ professional growth. They understand each team member’s talents and development opportunities.
- Quality Assurance and Call Monitoring: They review conversations, evaluate agent effectiveness, and verify quality benchmarks are achieved. They identify issues and deliver timely guidance. They also manage complex calls that agents cannot handle independently.
- Schedule Management and Staffing: They coordinate daily rosters, process leave applications, and maintain appropriate coverage levels. When someone reports illness, they secure replacements. When call demand exceeds projections, they modify breaks and assignments.
- Team Communication and Morale: They serve as the primary liaison between agents and senior management. They facilitate staff meetings, relay policy updates, and strive to sustain positive team dynamics. They acknowledge achievements and resolve issues before they escalate into larger challenges.
Best Practices in Call Center Management
Every company wants to deliver exceptional service to its customers. But it doesn’t happen overnight. You need to follow certain practices that will help your call center management efforts:
1. Define Clear Goals And KPIs
Don’t just set goals for your call center agents. Explain why they matter.
you tell agents you want to answer calls within 20 seconds, you need to explain that customers start getting frustrated after 30 seconds. When you aim for 80% first call resolution, you need to show them how callbacks create more work for everyone and annoy customers.
You must post your main goals where everyone can see them. Track progress daily, but don’t make it feel punitive. Sometimes you need to adjust targets. If industry standards change or your business model shifts, the goals should shift too. Don’t stick with outdated metrics just because that’s how you have always done it.
2. Use Technology And Automation
Technology should make your agents’ jobs easier, not harder. Some companies buy expensive systems that nobody uses because they’re too complicated or don’t actually solve real problems.
Cloud-based systems give you flexibility. Advanced features don’t matter if your team cannot figure out how to use them. Here’s what actually helps: good call routing that gets customers to the right person quickly, CRM systems that show customer history at a glance, and knowledge bases that agents can search during calls.
Don’t automate everything just because you can. During customer interactions, they can tell when they’re talking to someone reading a script versus someone who actually understands their problem.
3. Prioritize Agent Engagement And Motivation
Unhappy agents create unhappy customers. A Gallup report states that 66% of employees are suffering, and 8% are struggling in their workplace. Recognition matters more than you’d think. When someone handles a difficult situation well, tell them right away. Public recognition in team meetings works great, but the immediate appreciation is different.
Career development is not just about promotions. Maybe one agent wants to learn more about technical issues. Another is interested in training new hires. Give people opportunities to grow, even if it’s not up the traditional ladder. And listen when agents tell you about problems. They are on the front lines. They know which processes are broken, which tools don’t work, and what customers actually complain about.
4. Provide Continuous Training And Feedback
One training doesn’t work in a call center. Things change too fast.
Do short, focused training sessions regularly. Maybe 15 minutes on handling a specific type of call. Or a quick refresher on a policy change. Keep it relevant and keep it moving.
Feedback should happen in real time when possible. Don’t wait for the quarterly review to tell someone they’re doing something wrong. But also don’t only give feedback when there’s a problem. Also appreciate and acknowledge people for why they do things right.
5. Ensuring Compliance & Security
Depending on your industry, compliance is not optional. Healthcare, finance, and education– they all have rules you need to follow.
Make compliance training practical. Using call center data, show agents exactly what to do in real situations. Document everything. If something goes wrong and you can’t prove you followed proper procedures, you will be in legal trouble.
Call Center Performance Management Metrics
Successful call center managers take some metrics for both outbound and inbound call centers seriously. These metrics help them manage call center operations smoothly:
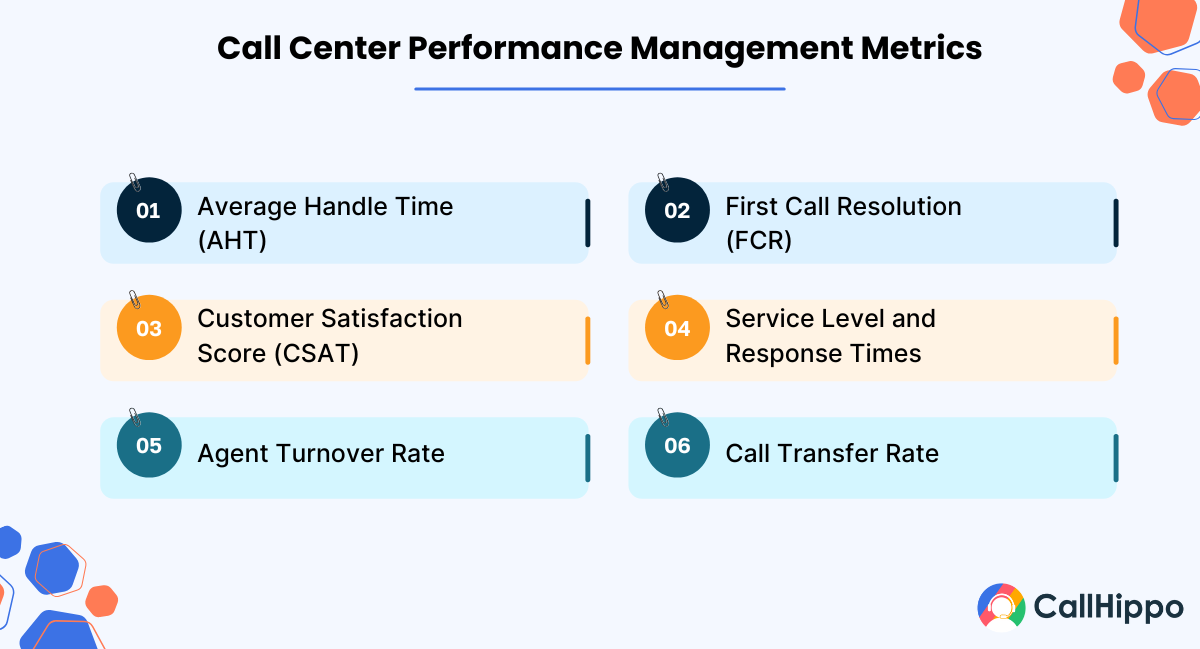

1. Average Handle Time (AHT)
AHT measures how long agents spend on each interaction – talk time, hold time, and wrap-up time combined. Good AHT depends on what kind of calls you handle. Technical support naturally takes longer than simple account updates. Set realistic targets based on call complexity.
Formula To Calculate Average Handle Time (AHT)
- AHT = (Total Talk Time + Total Hold Time + Total After-Call Work Time) / Total Number of Interactions
2. First Call Resolution (FCR)
FCR tracks how often you completely resolve a customer’s issue on the first try. It is one of the most important metrics for customer satisfaction.
When customers don’t have to call back, they’re happier. Your call volume stays manageable. And your agents feel better about their work because they’re actually helping people.
To improve FCR, make sure agents have access to all the information they need. Train them thoroughly on common issues. And give them enough authority to actually fix problems instead of just documenting them.
Formula To Calculate First Call Resolution (FCR)
- FCR Rate = (Number of issues resolved on the first contact / Total number of issues) × 100%
3. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
CSAT measures how happy customers are with their service experience. Usually on a 1-5 scale.
You can send surveys right after interactions while the experience is fresh. Keep them short – three questions maximum. Ask specific questions about the service, not general company satisfaction.
Use CSAT data to identify patterns. If one agent consistently gets low scores, they need coaching. If everyone scores poorly on a specific call type, maybe the process needs work.
Formula To Calculate Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- CSAT % = (Number of satisfied customers / Total number of survey responses) × 100
4. Service Level and Response Times
Service level measures what percentage of calls you answer within your target time. The industry standard is usually 80% of calls within 20 seconds.
This directly impacts everything else. When people wait on hold too long, they’re frustrated before the call even starts. Monitor this throughout the day, not just at the end.
If service levels drop, figure out why quickly. Maybe you need more agents scheduled. Maybe the call routing system isn’t working right. Don’t let it slide; improve it at the earliest.
Formula To Calculate Service Level (SL)
- SL % = (Number of calls answered within the target timeframe / Total number of calls received) × 100%
5. Agent Turnover Rate
High turnover negatively impacts your operation. Every time someone leaves, you lose their knowledge and experience. Training new people is expensive and time-consuming.
Track both voluntary and involuntary turnover. Exit interviews help you understand why people are leaving. If everyone mentions the same problems, those are your priorities to fix.
Formula To Calculate Agent Turnover Rate
- Turnover Rate % = (Number of agents who left / Average number of agents during the period) × 100
6. Call Transfer Rate
This shows how often agents transfer calls to someone else. Some transfers are necessary, but too many usually mean problems.
High transfer rates might mean agents aren’t trained well enough to handle common issues. Or maybe your call routing is sending people to the wrong department initially.
Work on reducing unnecessary transfers. It frustrates customers and wastes time for everyone involved.
Formula To Calculate Call Transfer Rate
- Call Transfer Rate % = (Total number of transferred calls / Total number of handled calls) × 100
DID YOU KNOW?
- 75% of leaders collaborate with external partners so that they can evolve their CX operations.
Challenges in Call Center Management and How to Overcome Them
Every call center faces similar problems. Here’s how you can overcome the call center challenges:
1. High Employee Turnover
You can reduce turnover if you approach it right. First, hire people who actually want to help customers. You can teach technical skills. Empathy and patience are harder to develop.
Create real career paths. Show agents how they can advance within your company. Promote from within when possible. When people see a future, they stay around longer. Make the job as pleasant as possible. Good tools, comfortable workspace, reasonable policies. Treat people like adults who want to do good work.
2. Handling Peak Call Volumes
Some days bring unexpected calls. A service outage, a viral social media complaint, a product recall, and your phones are ringing nonstop. Plan for these situations. Cross-train agents so they can help with different call types and deliver high-quality customer service. Have a list of part-time or contract agents you can bring in quickly.
Consider offering callbacks during busy periods. Most customers prefer this to sitting on hold for 30 minutes. Use your website and social media to provide updates during major issues
3. Balancing Automation With Human Interaction
Technology can handle routine tasks, but customers still need human help for complex problems.
Use automation strategically. Let chatbots handle simple questions like store hours or basic account information. Use automated systems to route calls efficiently.
But make it easy to reach a human when needed. Don’t make customers jump through ten menu options to talk to someone. Despite all the tech advances, people still prefer talking to real agents for anything complicated.
4. Maintaining Compliance And Data Security
Data breaches and compliance violations pose a threat to your business. Take this seriously from the beginning. Train everyone on security procedures. Regularly audit your systems and processes. Keep software updated. Monitor access to sensitive information.
Make compliance ongoing, not just a one-time training session. Test agents regularly on procedures. Update agent training when regulations change.
Tools and Software Required for Call Center Management
The right tools make managing your operation much easier. Here’s what you actually need.
1. Call Center Monitoring Tools
Call center monitoring tools help you track performance and quality in real time. You can listen to live calls, review recordings, and score agent performance.

Look for call center software that integrates with your phone system and provides clear, actionable reports. Real-time dashboards help you spot problems in both inbound and outbound calls before they become crises.
2. Workforce Management Software
This helps with scheduling, forecasting, and tracking performance. Good workforce management software predicts call volumes and suggests optimal staffing levels.
These tools help ensure you have the right number of people at the right times. They also track schedule adherence and break compliance.
3. CRM And Analytics Platforms
Customer relationship management systems store all customer information in one place. Agents can see interaction history, account details, and preferences instantly.

Analytics platforms help you understand trends in your data. Which products generate the most support calls? Which agents are most successful? What time of day is busiest?
4. AI and Automation Solutions
Artificial intelligence can help with call routing, matching customers with the best agents for their specific needs. Speech analytics can analyze recorded calls for insights you might miss. But use AI to support your agents, not replace them. The technology should make their jobs easier and help them serve customers better.

Future Of Call Center Management
The industry keeps evolving. Here’s what is coming that will change how we manage call centers.
1. Omnichannel Support Integration
Customers want to start a conversation on chat, continue it over email, and finish with a phone call – all while having agents remember the entire context. This requires integrated systems that share information across all channels. Your agents need training on every communication method, not just phone skills.
2. AI-Powered Performance Insights
Artificial intelligence will give us deeper insights into agent performance and customer sentiment. It can identify coaching opportunities and predict which customers might have problems. These tools will help managers make better decisions about training, scheduling, and resource allocation.
3. Remote and Hybrid Call Center Models
Call centers are embracing remote work. Remote work requires different management approaches. You need better technology for monitoring and communication. Training and coaching must work in virtual environments.
Conclusion
The best call center management tips are not about fancy technology or complex metrics. They are about creating an environment where agents feel supported, customers feel heard, and problems get solved efficiently.
You’ll face challenges – high turnover, difficult customers, system outages, and budget pressures. But when you focus on the fundamentals – good training, clear expectations, proper tools, and genuine care for your team – most problems become manageable.
Remember that call center performance management is an ongoing process. Customer expectations change. Technology evolves. Your team grows and develops. Stay flexible and keep learning.
FAQs
1. What is the role of call center management?
The role of call center management is to oversee every aspect of a customer service operation. You need to hire agents, monitor performance, ensure quality, manage technology, and maintain customer satisfaction. You need to coach agents, handle escalated customer issues, and plan staffing schedules. The role requires balancing customer needs, business objectives, and employee satisfaction.
2. What are the most important call center management skills?
The most important call center management skills are strong communication, analytical thinking, and leadership abilities. You need to interpret data, make quick decisions, and solve problems under pressure. Empathy is crucial for working with both frustrated customers and stressed agents. Time management and multitasking are essential, too.
3. How do you manage call center performance effectively?
To manage call center performance effectively, start with clear, realistic goals. Monitor key metrics like first call resolution, average handle time, and customer satisfaction. Give regular coaching and feedback. Invest in proper training and make sure agents have the tools they need.
Published : September 22, 2025

Ananya Dubey, Sales Manager at CallHippo, brings years of SaaS sales experience. She specializes in business communication solutions, call center software, and building long-term relationships that drive growth for mid-market and enterprise clients.


Let’s Stay in Touch
Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.
![]()
![]() +24K people have already subscribed
+24K people have already subscribed
Source



